Pythagoras Theorem Proof
Pythagoras Theorem Statement
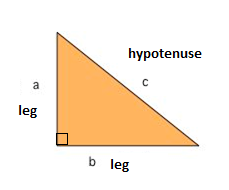
Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. The sides of this triangles have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse. Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side, as it is opposite to the angle 90°. The sides of a right triangle (say x, y and z) which has positive integer values, when squared are put into an equation, also called a Pythagorean triple.
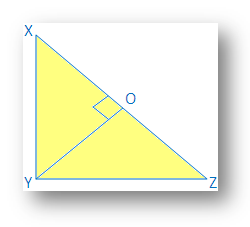
Proof: First, we have to drop a perpendicular BD onto the side AC
We know, △ADB ~ △ABC
Therefore, ADAB=ABAC (Condition for similarity)
Or, AB2 = AD × AC ……………………………..……..(1)
Also, △BDC ~△ABC
Therefore, CDBC=BCAC (Condition for similarity)
Or, BC2= CD × AC ……………………………………..(2)
Adding the equations (1) and (2) we get,
AB2 + BC2 = AD × AC + CD × AC
AB2 + BC2 = AC (AD + CD)
Since, AD + CD = AC
Therefore, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Hence, the Pythagorean thoerem is proved.
Note: Pythagorean theorem is only applicable to Right-Angled triangle.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You For Visit To My Blog ...
you will soon get the reply.. for your comment.......