Transformer Formula and Wave Speed Formula
What is Transformer?
The transformer transforms the energy from one electrical circuit to another. This occurs by using electromagnetic induction. It is known as an efficient voltage converter, and it can reduce the high voltage to low voltage and vice versa. A good-condition transformer consists of two windings, which primary winding and secondary are winding. There are two types of the transformer which are step up and step down transformers. In this article, we will discuss the transformer formula with examples. Let us learn the concept!
Transformer Formula
What is a Transformer?
The transformer is an electrical device that allows us to increase or decrease the voltage in an alternating current electrical circuit, maintaining power. The power that enters the equipment, in the case of an ideal transformer, is equal to that obtained at the output.
Real machines have a small percentage of losses. It is a device that converts the alternating electrical energy of a certain voltage level into alternating energy of another voltage level, based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
It is made up of two coils of conductive material, wound on a closed nucleus of ferromagnetic material, but electrically isolated from each other. The only connection between the coils is the common magnetic flux established in the core. The coils are called primary and secondary according to the input or output of the system in question, respectively.
Transformer Formula
The value of the power for an electric circuit is the value of the voltage by the value of the current intensity. As in the case of a transformer, the value of the power in the primary is the same value for the power in the secondary we have:
(input voltage on the primary coil) × (input current on the primary coil ) = (output voltage on the secondary coil ) × (output current on the secondary coil)
This can be written as an equation:
We can also work out the transformer output voltage if we know the input voltage and the number of turns on the primary and secondary coils.
This can be written as an equation:
Where,
| input voltage on the primary coil. | |
| input voltage on the secondary coil. | |
| input current on the primary coil. | |
| input current on the secondary coil. | |
| the number of turns of wire on the primary coil. | |
| the number of turns of wire on the secondary coil. |
Solved Examples
Q. 1: We have a transformer with a current in the primary coil of 10 A and input voltage in the primary coil of 120 V, if the voltage in the output of the secondary coil is 50 V, calculate the current in the output of the secondary coil.
Solution: As we have to determine the output current in the secondary coil, we will the first equation i.e.
As given,
Putting values given in the question:
= 24 A
Therefore, current in the output of the secondary coil is 24 A.
Wave Speed Formula
A wave is a disturbance that moves along a medium from one end to the other. We can watch an ocean wave moving along the medium i.e. the ocean water. Also, we may observe that the crest of the wave is moving from one location to another over a given interval of time. This crest is observed to cover the distance. As we know that the speed of an object refers to how fast that object is moving and is usually expressed as the distance traveled per unit time of travel. In this topic, we will discuss the wave speed formula with examples. Let us learn the concept!
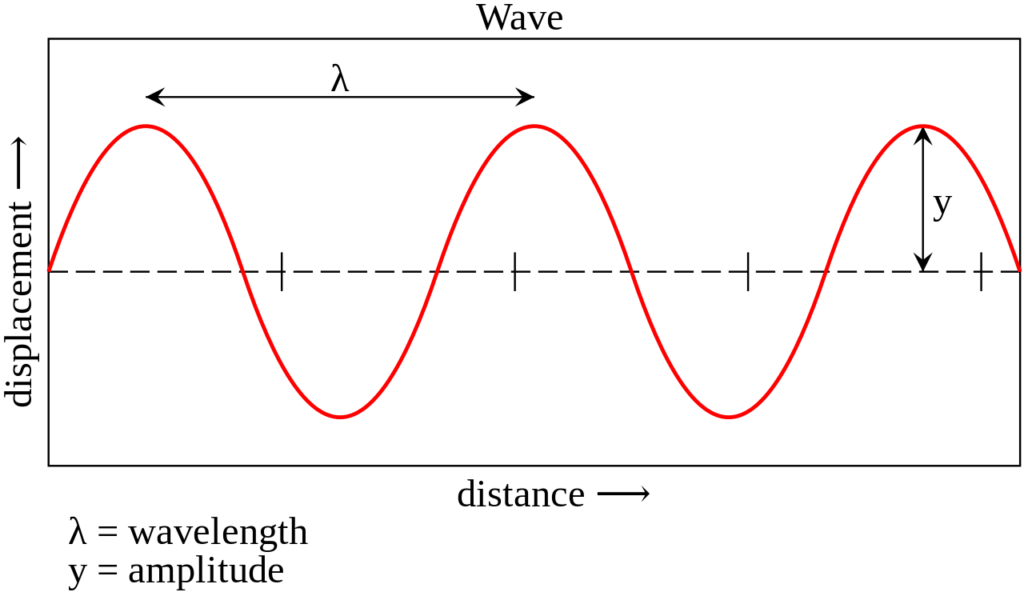
Wave Speed Formula
What is a wave?
A wave is a kind of disturbance in a moving medium. Waves of the ocean move in a medium and we can see the movement of the wave from one point to the other. One can describe the motion of an object regarding the speed which describes the velocity of the object.
This wave is visualized when a source vibrates and disturbs a particle in the medium. We can also see it in the case of tuning fork or ripples in water when a body is dropped, etc.
Sometimes a wave may encounter the end of a medium. Wave introduced by someone into one end of a slinky will travel through it. Eventually, it will reach the end of the slinky and the presence of the hand of a second person. One important behavior of waves undergo at the end of a medium is the reflection. The wave will reflect on the person’s hand. When a wave undergoes reflection, it remains within the medium and merely reverses its direction of travel.
The number of waves traveled in one second is its frequency. Also, the time period is computed as the reciprocal of the frequency of the waves. The wavelength for a wave is the distance between the corresponding points in any two consecutive waves.
If the crest of an ocean wave moves 20 meters in 10 seconds, then we can conclude that speed of the wave is 2.0 m/s. Also, if the crest of an ocean wave moves a distance of 25 meters in 10 seconds, then the speed of the wave is 2.5 m/s.
Formula
It involves wavelength and frequency of the wave, and is given by,
v = f × \lambda
Where,
| v | the velocity of the wave |
| f | frequency of the wave |
| \lambda | wavelength. |
Solved Examples
Q.1: A light wave travels with the wavelength 600 nm, then find out its frequency.
Solution:
Given in the problem,
Wavelength, \lambda = 600 nm,
Speed of light, v = 3 × 10^8 m/s.
The frequency is:
f = \frac{v}{\lambda }\\
f = \frac{3 × 10^8 }{ 600 × 10^-^9}\\
= 5 × 10^1^4 Hz.
The frequency of the light wave is 5 \times 10^1^4 Hz.
Q.2: A sound wave has a wavelength of 1.5 mm, then find out its frequency.
Solution:
Given:
Wavelength, \lambda = 1.5 mm,
Speed of sound, v = 343.2 m/s.
The frequency is:
f = \frac{v}{\lambda }\\
f = \frac{343.2}{ 1.5 × 10^-^2}
= 22.8 KHz.
The frequency of the sound waves is 22.8 kHz.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You For Visit To My Blog ...
you will soon get the reply.. for your comment.......